E-Bike Battery Consumption: What Affects It and How to Extend Your Range
- tanja548
- Nov 16
- 4 min read
Updated: Nov 29

E-bikes combine the comfort of electric assistance with the joy of exploration. But many riders ask themselves the same question: Why can I sometimes ride 100 km on one charge, and other times only 60?
The answer is simple – e-bike battery consumption depends on multiple factors: terrain, weather, rider weight, cadence, motor efficiency, and the battery’s condition.
Research by Nikolov (2023) and Burani et al. (2022) confirms that energy consumption can vary by up to 50% even when using the same equipment.
Key Factors Affecting E-Bike Battery Consumption
Technical Factors
Motor Type and Position
Mid-drive motors (Bosch, Brose, Shimano) are more efficient, as they distribute weight evenly and transfer power more effectively.
Hub motors are simpler but consume more energy, especially on climbs.
Environmental Factors
Terrain Incline: A 10% uphill grade can increase consumption by up to 40%.
Wind Resistance: Energy use rises exponentially with speed – headwinds can double consumption.
Temperature: At 0°C, lithium-ion batteries may lose up to 20% of their capacity.
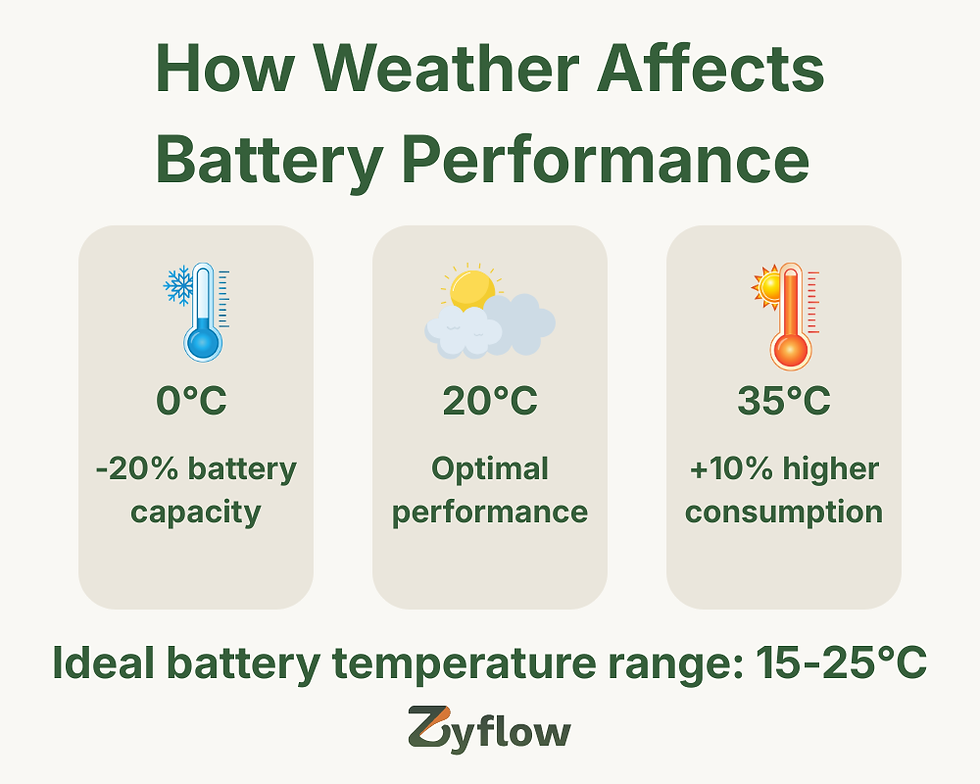
Infographic: Weather Impact on Battery Performance
Riding Style
Assist Level: Turbo or Boost modes can triple power draw compared to Eco mode.
Cadence and Acceleration: Smooth pedaling (70–90 rpm) saves energy; rapid acceleration drains it faster.
Maintenance: Proper tire pressure and a clean drivetrain reduce mechanical resistance.

Infographic: Factors That Drain or Save Energy
Motor Efficiency Explained
An e-bike motor doesn’t work with equal efficiency at all cadences (pedaling speeds). Manufacturers such as Bosch, Shimano, and Brose have measured an efficiency curve – a graph showing how much electrical energy is converted into mechanical power.
According to Nikolov (2023) and lab tests by Bosch Engineering and EMTB Forums, the following applies:
Cadence (rpm) | Efficiency (%) | Description | Impact on Battery |
< 50 rpm | ~60% | Low speed / high torque | +20–25% consumption |
60–70 rpm | ~75–80% | Beginning of optimal range | Normal consumption |
70–90 rpm | 85–90% | Optimal efficiency range | –10–15% consumption |
> 100 rpm | ~70–75% | Over-rotation, lower torque | +10–20% consumption |
> 110 rpm | <65% | Inefficient, heat loss | +25–30% consumption |
Summary: Bosch and Brose motors reach peak efficiency (85–90%) between 70–90 rpm. Below 60 rpm or above 100 rpm, energy use rises by 15–30% for the same power output.
Why It Happens: E-bike motors contain internal gears and sensors that work best at certain rotational speeds.
At low cadence (<60 rpm), the motor draws high current → more heat and energy loss.
At high cadence (>100 rpm), the rotor spins too fast for the magnetic field → reduced efficiency.
Between 70–90 rpm, voltage, current, and torque stay in balance.
What This Means for Riders: Riding in the optimal cadence zone:
reduces average energy use by 10–20%,
prevents motor overheating,
extends battery life,
and results in a smoother, quieter ride.
That’s why modern systems (Bosch, Brose, Shimano) integrate torque + cadence sensors, automatically adjusting assistance to maintain peak efficiency.

Infographic: Motor Efficiency and Battery Impact
Average Consumption and Realistic Range
Based on simulations and real-world testing, the average consumption is between 0.32–0.4 Ah/km. Here’s how battery capacity affects range:

Infographic: Battery Capacity vs. Real Range
How to Reduce Energy Use
Choose assist levels wisely – use Turbo only on steep climbs.
Maintain steady cadence (70–90 rpm).
Check tire pressure before every ride.
Clean the drivetrain regularly.
Avoid carrying unnecessary weight

Infographic: Tips to Ride Smarter and Extend Range
Final Takeaway
E-bike range is not fixed – it depends on how you ride and in what conditions.
As Bosch eBike Systems engineers emphasize, understanding your cadence, assist level, and terrain can improve your range by up to 20%.

Call to Action for Engineers, Developers & Technical Experts
If you work in any of the following areas:
motor and drivetrain engineering
battery systems, BMS technology or efficiency testing
IoT connectivity and smart-charging solutions
e-bike infrastructure development and planning
technical standards, certification or compliance
fire safety, thermal monitoring or risk analysis
data modelling, energy consumption analysis or sensor technologies
…we’d love to hear from you.
Reach out and share your expertise, insights, or emerging innovations with us.
Your knowledge can help:
improve the safety and efficiency of e-bike technology,
shape better infrastructure for riders,
support tourism destinations and municipalities, and
strengthen the entire e-bike ecosystem.
At Zyflow, we are building an open, collaborative space where technical experts, infrastructure creators, and e-bike users come together to drive the future of electric mobility.
Zyflow Vision: Empowering Smarter, Safer and Data-Driven E-Biking
At Zyflow, our mission is to make e-biking easier, safer, and more informed for every rider. We believe that e-cyclists deserve access to clear, accurate, and practical information — not only about battery consumption and motor efficiency, but also about the infrastructure, services, and technologies that support them on the road.
We are building a connected digital ecosystem that unites data for everyday e-bike users, tourism operators, infrastructure planners, and the growing community of innovators developing new technologies. By sharing research-based insights, technical knowledge, and real-world findings, we aim to help riders make smarter decisions — and help the creators of e-bike friendly infrastructure design better, safer, and more intuitive solutions.
Our vision is a world where:
every e-cyclist understands their e-bike,
every route is supported with reliable charging and safety information, an
every technological innovation finds its way to the people who need it most.
With Zyflow, knowledge becomes the foundation of safer and more sustainable electric mobility.
References
Nikolov, A. (2023). Energy Consumption and Efficiency Modelling of Electrically Assisted Bicycles.
Burani, N., Cabri, G., & Leoncini, M. (2022). Electrically Assisted Bicycles: Experimental Characterization and Power Consumption Analysis.
Bosch eBike Systems – Technical Overview
Brose eBike Systems – Drive S Mag Efficiency Curves
Shimano STEPS – Efficiency Data
EMTB Forums (2023). Bosch Performance Line CX Efficiency Tests
Ebike24 Blog (2024). Understanding E-bike Battery Consumption



Comments